How to batch convert heic files to jpg or other image formats
If you are not a programmer or not familar with computer setting stuff, just head to here
1. Check your image files’ depth bit
If you are not using Windows, you can skip this part.
If you look at the images’ properties, you can see what “Bit depth” of your file is.
Mostly, it will be 32 bits (RGBA) unless you changed settings.
2. Install ImageMagick
Install a proper ImageMagick build depends on your operating system. ImageMagick
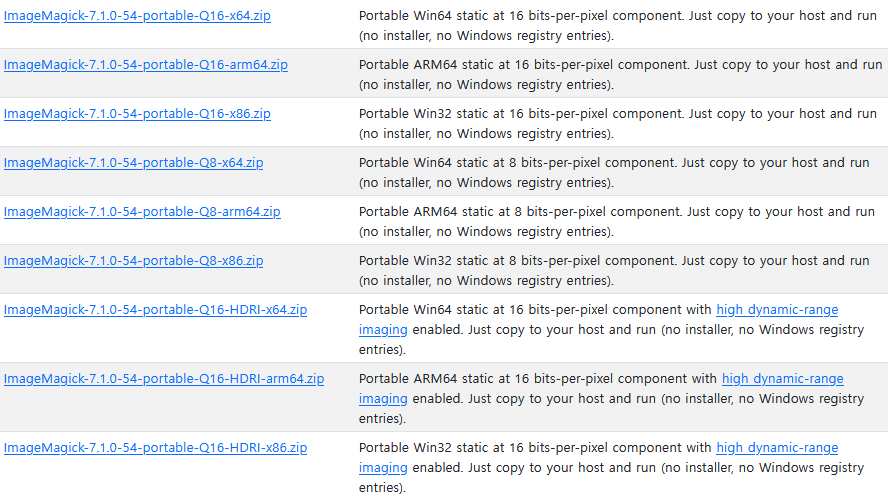
For Windows, you need to download a specific build that supports higher depth bit as we checked at #1. If you have images of 24 or 32 bits, just download 16 bits binary.
In most of cases, you need Q16-x64 or Q16-arm64.
For Macs, use brew install imagemagick. The simplest option.
Once you installed or download the portable version, add to Environment Variable PATH so that python script can access it. Or just put the portable file along with the python script below.
$ ./magick.exe
Error: Invalid argument or not enough arguments
Usage: magick.exe tool [ {option} | {image} ... ] {output_image}
Usage: magick.exe [ {option} | {image} ... ] {output_image}
magick.exe [ {option} | {image} ... ] -script {filename} [ {script_args} ...]
magick.exe -help | -version | -usage | -list {option}
3. Run python script
Put the script along with your images and run it. You can pass -o or --output option for the specific output format, -i or --input for the specific input format as well.
import os, subprocess
from sys import platform
from optparse import OptionParser
directory = '.'
def convert_formats_to_formats(input, output):
input_format_string = "." + input.strip().replace('.', '')
output_format_string = "." + output.strip().replace('.', '')
if not os.path.exists("output"):
os.mkdir("output")
for filename in os.listdir(directory):
if not filename.lower().endswith(input_format_string):
continue
print('Converting %s...' % os.path.join(directory, filename))
magick_command = ""
if platform == "linux" or platform == "linux2":
magick_command = "magick"
elif platform == "darwin":
magick_command = "magick"
elif platform == "win32":
magick_command = "magick.exe"
subprocess.run([magick_command, "%s" % filename, "output/%s" % (filename[0:-5] + output_format_string)])
continue
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = OptionParser()
parser.add_option("-i", "--input", action="store", dest="input_format", help="Specify conversion format. Default is heic", default="heic")
parser.add_option("-o", "--output", action="store", dest="output_format", help="Specify conversion format. Default is jpg", default="jpg")
(options, args) = parser.parse_args()
convert_formats_to_formats(input=options.input_format, output=options.output_format)
If you want a simple binary file for this, you can use pyinstaller
pip install pyinstaller
pyinstaller --onefile image_to_image.py
Happy Hacking!

Leave a comment